Sublime Text Cheat Sheet, Windows Cheat Sheet, Sublime Text 2, Mac Cheat Sheet, GitHub Cheat Sheet, Org-Mode Cheat Sheet, Code Cheat Sheet, Sublime Text Icon, Shortcut Cheat Sheet, Epic Keyboard Shortcuts Cheat Sheet, Perl Cheat Sheet, OS X Cheat Sheet, Windows Shortcut Keys Cheat Sheet, AOE Hot Key Cheat Sheet, Symbol Font Cheat Sheet, Mac Terminal Cheat Sheet, Cheat Sheet Design, Ruby Cheat.
I’ve compiled a list of essential Vim commands that I use every day. I have then given a few instructions on how to make Vim as great as it should be, because it’s painful without configuration.
Essentials
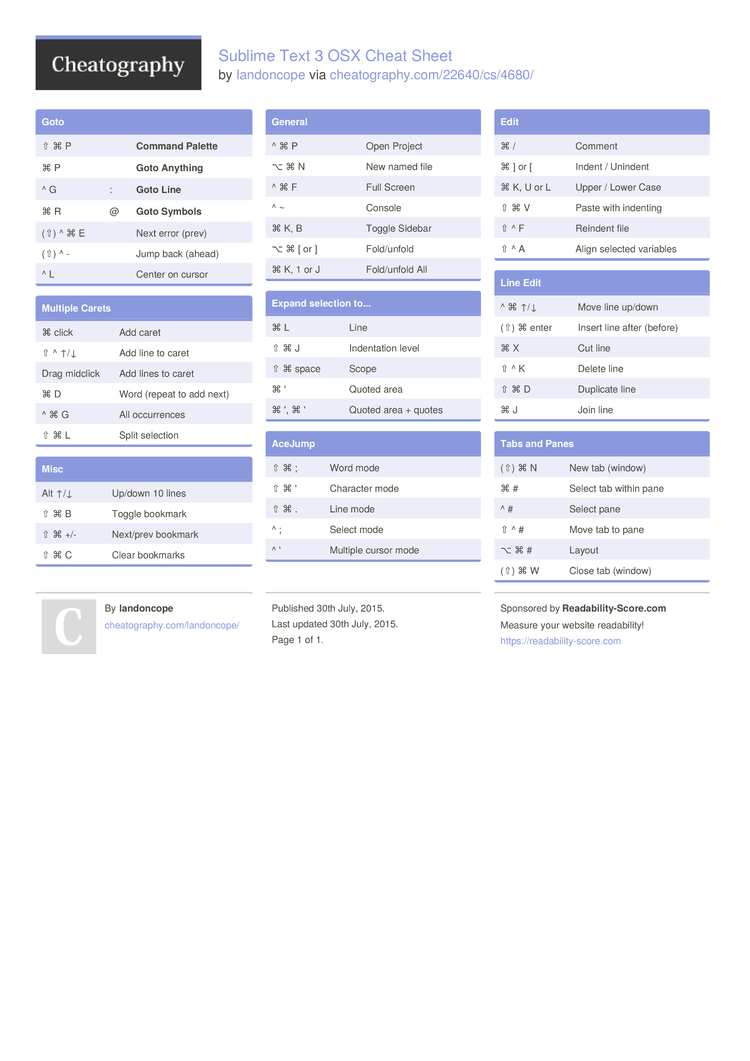
Sublime Text 3 Keyboard Shortcuts by tdeyle - Cheatography.com Created Date: 1933Z. Sublime Text 3 cheat sheet of all shortcuts and commands.
- SUBLIME TEXT 3 CHEAT SHEET 4 months ago SK. Sublime Text 3 is the latest version of one of the most commonly used plain text editors by web developers, coders, and programmers. There are some shortcuts, You might know about them.
- Sublime Text Cheat Sheet for development, editing, testing, deployment for Ruby on Rails. +1 (212) 520-1413 +91.9004 210 210; icicle.tech; hello@icicletech.com.
Cursor movement (Normal/Visual Mode)
hjkl- Arrow keysw/b- Next/previous wordW/B- Next/previous word (space seperated)e/ge- Next/previous end of word0/$- Start/End of line^- First non-blank character of line (same as0w)
Sublime Text 3 Cheat Sheet Pdf
Editing text
i/a- Start insert mode at/after cursorI/A- Start insert mode at the beginning/end of the lineo/O- Add blank line below/above current lineEscorCtrl+[- Exit insert moded- Deletedd- Delete linec- Delete, then start insert modecc- Delete line, then start insert mode
Operators
- Operators also work in Visual Mode
d- Deletes from the cursor to the movement locationc- Deletes from the cursor to the movement location, then starts insert modey- Copy from the cursor to the movement location>- Indent one level<- Unindent one level- You can also combine operators with motions. Ex:
d$deletes from the cursor to the end of the line.
Marking text (visual mode)
v- Start visual modeV- Start linewise visual modeCtrl+v- Start visual block modeEscorCtrl+[- Exit visual mode
Clipboard
yy- Yank (copy) a linep- Paste after cursorP- Paste before cursordd- Delete (cut) a linex- Delete (cut) current characterX- Delete (cut) previous characterd/c- By default, these copy the deleted text
Exiting
:w- Write (save) the file, but don’t quit:wq- Write (save) and quit:q- Quit (fails if anything has changed):q!- Quit and throw away changes
Search/Replace
/pattern- Search for pattern?pattern- Search backward for patternn- Repeat search in same directionN- Repeat search in opposite direction:%s/old/new/g- Replace all old with new throughout file (gn is better though):%s/old/new/gc- Replace all old with new throughout file with confirmations

General
u- UndoCtrl+r- Redo
Advanced
Cursor movement
Ctrl+d- Move down half a pageCtrl+u- Move up half a page}- Go forward by paragraph (the next blank line){- Go backward by paragraph (the next blank line)gg- Go to the top of the pageG- Go the bottom of the page: [num] [enter]- Go to that line in the documentctrl+e / ctrl+y- Scroll down/up one line
Character search
f [char]- Move forward to the given charF [char]- Move backward to the given chart [char]- Move forward to before the given charT [char]- Move backward to before the given char;/,- Repeat search forwards/backwards
Editing text
J- Join line below to the current oner [char]- Replace a single character with the specified char (does not use Insert mode)
Visual mode
O- Move to other corner of blocko- Move to other end of marked area
File Tabs
:e filename- Edit a file:tabe- Make a new tabgt- Go to the next tabgT- Go to the previous tab:vsp- Vertically split windowsctrl+ws- Split windows horizontallyctrl+wv- Split windows verticallyctrl+ww- Switch between windowsctrl+wq- Quit a window
Marks
- Marks allow you to jump to designated points in your code.
m{a-z}- Set mark {a-z} at cursor position- A capital mark {A-Z} sets a global mark and will work between files
'{a-z}- Move the cursor to the start of the line where the mark was set'- Go back to the previous jump location
Text Objects
- Say you have
def (arg1, arg2, arg3), where your cursor is somewhere in the middle of the parenthesis. di(deletes everything between the parenthesis. That says “change everything inside the nearest parenthesis”. Without text objects, you would need to doT(dt).
General
.- Repeat last commandCtrl+r + 0in insert mode inserts the last yanked text (or in command mode)gv- reselect (select last selected block of text, from visual mode)%- jumps between matching()or{}
Vim is quite unpleasant out of the box. It’s an arcane experience:
- Autocomplete is missing
- System clipboard is not used
- Act of typing
:wto save is cumbersome - Mouse doesn’t work
- Management of multiple files is tricky
- Ability to indent multiple lines is missing
It does have a significant strength though: your fingers can stay on the main keyboard keys to do most editing actions. This is faster and more ergonomic. I find that the toughest part about VIM is guiding people towards getting the benefits of VIM without the drawbacks. Here are two ideas on how to go about this.
Switch caps lock and escape
- I highly recommend you switch the mapping of your caps lock and escape keys. You’ll love it, promise! Switching the two keys is platform dependent.
Visual Studio Code
- VSCode is the simplest way to give you a fantastic editor that also gives you the benefits of VIM. Just install the VIM extension.
- I made a few slight changes which improved the experience for me.
Configure native VIM
For all the given limitations, you’ll need to find a solution. You can either solve the issues one by one, or you can use a reference .vimrc settings file that fix most of the issues out-of-the-box.

- My .vimrc file could be a good starting point. Honestly, it’s a bit old and not the best. I now use VSCode mainly so I haven’t kept a great vimrc.

Using the system clipboard
'+ycopy a selection to the system clipboard'+ppaste from the system clipboard- If this doesn’t work, it’s probably because Vim was not built with the system clipboard option. To check, run
vim --versionand see if+clipboardexists. If it says-clipboard, you will not be able to copy from outside of Vim.- For Mac users, homebrew install Vim with the clipboard option. Install homebrew and then run
brew install vim.- then move the old Vim binary:
$ mv /usr/bin/vim /usr/bin/vimold - restart your terminal and you should see
vim --versionnow with+clipboard
- then move the old Vim binary:
- For Mac users, homebrew install Vim with the clipboard option. Install homebrew and then run
Sublime Text
- Another option is to use Vintageous in Sublime Text (version 3). This gives you Vim mode inside Sublime. I suggest this (or a similar setup with the Atom editor) if you aren’t a Vim master. Check out Advanced Vim if you are.
- Vintageous is great, but I suggest you change a few settings to make it better.
- Clone this repository to
~/.config/sublime-text-3/Packages/Vintageous, or similar. Then check out the “custom” branch.- Alternatively, you can get a more updated Vintageous version by cloning the official repository and then copying over this patch.
- Change the user settings (
User/Preferences.sublime-settings) to include:'caret_style': 'solid'- This will make the cursor not blink, like in Vim.
- Sublime Text might freeze when you do this. It’s a bug; just restart Sublime Text after changing the file.
ctrl+rin Vim means “redo”. But there is a handy Ctrl + R shortcut in Sublime Text that gives an “outline” of a file. I remapped it to alt+r by putting this in the User keymap{ 'keys': ['alt+r'], 'command': 'show_overlay', 'args': {'overlay': 'goto', 'text': '@'} },
- Mac users: you will not have the ability to hold down a navigation key (like holding j to go down). To fix this, run the commands specified here: https://gist.github.com/kconragan/2510186
- Clone this repository to
- Now you should be able to restart sublime and have a great Vim environment! Sweet Dude.
Other
I don’t personally use these yet, but I’ve heard other people do!
:wqa- Write and quit all open tabs (thanks Brian Zick)
Additional resources
- Practical Vim is a fantastic resource on many of the useful hidden features of vim.
A cheat sheet about regular expressions in Sublime Text.
| expression | Description |
|---|---|
. | Match any character |
^ | Match line begin |
$ | Match line end |
* | Match previous RE 0 or more times greedily |
*? | Match previous RE 0 or more times non-greedily |
+ | Match previous RE 1 or more times greedily |
+? | Match previous RE 1 or more times non-greedily |
? | Match previous RE 0 or 1 time greedily |
?? | Match previous RE 0 or 1 time non-greedily |
A|B | Match either RE A or B |
{m} | Match previous RE exactly m times |
{m,n} | Match previous RE m to n times greedily |
{m, n}? | Match previous RE m to n times, no-greedily |
| expression | Description |
|---|---|
[abc] | Match either a, b or c |
[^abc] | Match any character not in this set (i.e., not a, b and c) |
[a-z] | Match the range from a to z |
[a-f2-8] | Match the range from a to z or the range from 2 to 8 |
[a-z] | Match a, - or z |
[a-] | Match a, - |
[-a] | Match -, a |
[-a] | Match -, a |
[{}*|()[]+^$.?] | Match either one of the chacters in []{}*|()+^$?. |
- Note that you can also use character class inside
[], for example,[w]matches any character inwordcharacter class.
“Multiple character” character class
An expression of the form [[:name:]] matches the named character class name.
| class name | Description |
|---|---|
alnum | Any alpha-numeric character |
alpha | Any alphabetic character. |
digit | Any decimal digit. |
xdigit | Any hexadecimal digit character. |
lower | Any lower case character. |
upper | Any upper case character. |
cntrl | Any control character1. |
print | Any printable character. |
punct | Any punctuation character. 2 |
space | Any whitespace character. 3 |
word | Any word character (alphanumeric characters plus the underscore). |
Note: To use upper and lower, you have to enable case sensitve search.
“Single character” character class
Sublime Cheat Sheet Pdf
| class name | Description |
|---|---|
d | Equal to [[:digit:]] |
l | Equal to [[:lower:]] |
u | Equal to [[:upper:]] |
s | Equal to [[:space:]] |
w | Equal to [[:word:]] |
D | Equal to [^[:digit:]] |
L | Equal to [^[:lower:]] |
U | Equal to [^[:upper:]] |
W | Equal to [^[:word:]] |
Defining capture groups
| expression | Description |
|---|---|
(?<NAME>pattern) | Define a regex group named NAME which you can later refer to with g{NAME} |
(?=pattern) | Positive lookahead, consumes zero characters, the preceding RE only matches if this matches |
(?!pattern) | Negative lookahead, consumes zero characters, the preceding RE only matches if this does not match |
(?<=pattern) | Positive lookbehind, consumes zero characters, the following RE will only match if preceded with this fixed length RE. |
(?<!pattern) | Negative lookbehind, consumes zero characters, the following RE will only match if not preceded with this fixed length RE. |
Refering to matching groups (capture groups)
| expression | Description |
|---|---|
1 | Refer to first regex group |
g{1} | Refer to first regex group |
g{12} | Refer to 12th regex group |
g{-1} | Refer to last regex group |
g{-2} | Refer to last but one regex group |
- The regex groups are indexed by the order of their opening braces.
- Note the
g{NUM}form allows for matching regex group index larger than 9, for example,g{12}.
Escapes
Sublime Cheat Sheet Mac
| class name | Description |
|---|---|
xdd | A hexadecimal escape sequence - matches the single character whose code point is 0xdd. |
x{dddd} | A hexadecimal escape sequence - matches the single character whose code point is 0xdddd. |
Word boundaries
The following escape sequences match the boundaries of words:
| class name | Description |
|---|---|
< | Matches the start of a word. |
> | Matches the end of a word. |
b | Matches a word boundary (the start or end of a word). |
B | Matches only when not at a word boundary. |
The title image is taken from here.
Control character explanation: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Control_character↩︎
There are 14 punctuation marks in English: https://grammar.yourdictionary.com/punctuation/what/fourteen-punctuation-marks.html↩︎
For whitespace character, see https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Whitespace_character↩︎
