- Access the ‘Zones’ tab on the ‘Network’ page and click ‘Add’ to create a new zone. Provide a name for the zone such as “GuestLAN” and a description. Select ‘LAN’ for the type and enable device access services as desired (i.e. Services you want users in the GuestLAN zone to be able to access on your Sophos XG device).
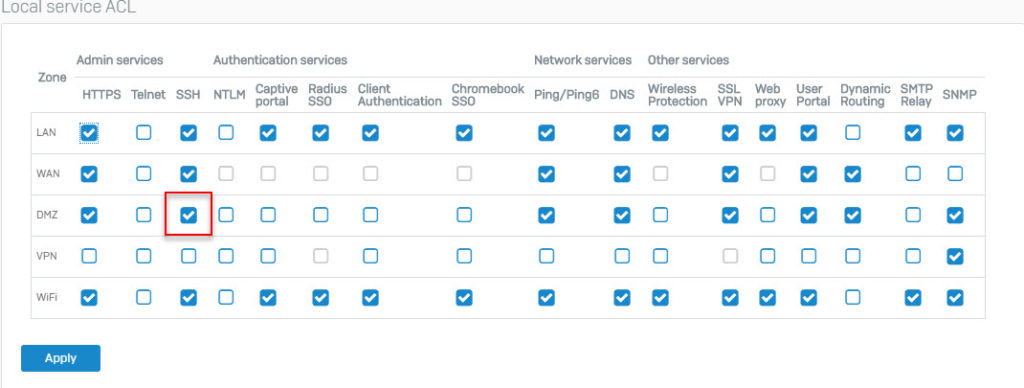
- Local Service ACL allows or denies access to specified services in a zone. For example, by default, Ping / Ping6 is disabled for the WAN area. A user from the internet tries to ping Sophos XG Firewall’s WAN IP. Because the Ping / Ping6 service is disabled for the WAN area, the packets will be dropped and therefore ping will fail.
- Checking the Sophos XG Advanced Shell reverseproxy.log File. To really see what is happening and what is being logged, we need to connect to the Sophos XG console. SSH to the device, enter the advanced shell and read the logs directly from /log/reverseproxy.log. Below is one of several entries that are generated when an attack is identified.
Confirm SSH Access on Sophos XG Ensure you can have enabled SSH access to the Sophos XG Firewall. If you are are accessing the device from a remote location, add an ACL exception rule. Overview Sophos allows remote shell access via SSH. PuTTY is a Windows SSH client, that may be used to sign in to the shell and access the Sophos command line environment remotely. Putty has many options and supports protocols other than SSH, but this article only shows the features necessary to connect to Sophos.
The server access assistant helps you create destination NAT (DNAT) rules for inbound traffic to internal servers.
Use this to create DNAT rules to translate incoming traffic to servers, such as web, mail, SSH, or other servers, and to access remote desktops. The assistant also creates a reflexive SNAT rule (for outbound traffic from the servers), a loopback rule (for internal users accessing the servers), and a firewall rule (to allow inbound traffic to the servers) automatically.Creating NAT and firewall rules that meet basic requirements using the server access assistant is a simple process. To add other rule settings, you can edit these rules later.
- Select the server access assistant from the following options:
- Go to Rules and policies > NAT rules. Select IPv4 or IPv6 and then select Add NAT rule. Select Server access assistant (DNAT).
- Go to Rules and policies > Firewall rules. Select protocol IPv4 or IPv6 and select Add firewall rule. Select New firewall rule Select Server access assistant (DNAT).
- Specify the settings:Option
Description Internal server IP address
To specify the internal server to access from the internet, select an internal IP host. Alternatively, you can enter a private IP address.
If you enter an IP address, XG Firewall automatically creates an IP host with the assigned name. You can change the name.
To specify more than one server, edit the rules later.
Public IP address
Select a public IP address or WAN interface. Alternatively, you can enter a public IP address.
If you enter an IP address, XG Firewall automatically creates an IP host with the assigned name. You can change the name.
To specify more than one public interface or IP address, edit the rules later.
Services
Select the services users can access on the internal server.
You can't create new services here. You can add them before you create the rules with the server access assistant or when you edit the rules later.
To specify port translation, edit the rules later.
External source networks and devices
Select the source networks and devices from which users can access the internal server.
To automatically create a loopback rule for internal users to access the server, select Any.
Save and finish
Review the settings and rules. Save the settings.
The server access assistant creates DNAT, reflexive SNAT, and loopback NAT rules for address translation and a firewall rule to allow inbound traffic to internal servers. The rules are added at the top of the NAT rule table and the firewall rule table and are turned on by default.
The reflexive and loopback rule names carry the name and rule ID of the DNAT rule created. The firewall rule name carries the DNAT rule name.
Restriction For automatically created loopback rules, XG Firewall sets the source networks and the inbound interface to Any. So, it doesn't create a loopback rule automatically when you specify the following settings in a single DNAT rule: External source networks and devices set to Any and the Public IP address set to a non-interface IP address (traffic reaching a non-interface IP address can flow through any inbound interface).For these settings, the loopback rule's source network and inbound interface would be the same as the DNAT rule's. Once the firewall matches traffic with the DNAT rule, it won't evaluate the loopback rule, which is listed below it, making the loopback rule redundant.
For these instances, you can create a DNAT rule manually to translate traffic between internal subnets.
Sophos Utm Ssh Access
What next
Sophos Xg Console Settings
- Reposition the rules in the NAT rule table and the firewall rule table to meet your requirements. XG Firewall evaluates rules from top down.
- Edit the rules to specify other settings, if required.
- Create a firewall rule to allow outbound traffic matching the reflexive NAT rule, if required.
